
Have you ever thought about how every software actively adapts to changing technology, user needs, and security? Adaptive software development is the optimal answer to this. Nowadays, software is highly futuristic and adaptive, but it doesn’t follow a blueprint to be this flexible. Businesses and every forward-thinking software development company adopt ASD principles to keep changing based on work environments and technologies. In this comprehensive blog, we will explore Adaptive Software Development, its benefits, weaknesses, and how businesses can execute it effectively.
Adaptive Software Development, aka ASD, is an iterative and flexible software development methodology that builds software while embracing uncertain changes and evolving requirements. It was developed by Jim Highsmith and Sam Bayer in the mid-1990s to effectively handle complex software calls. ASD emphasizes swift adaptability and a collaborative approach to respond to the dynamic environment. It works on continuous learning and serves quick upgradations as per the rapidly evolving needs of your project.
Listed below are the key reasons why people prefer ASD:
ASD helps in identifying risks in the development process through iterative feedback and stakeholder communication at each cycle.
ASD keeps testing during the development process for innovative outcomes.
ASD focuses on user needs and wants in the development process.
Here are the top qualities of Adaptive Software Development that make it unique from others:
ASD works on a flexible development instead of a fixed and sequenced structure. It adapts software based on changing environments.
ASD learns continuously about product needs and feedback to refine the product and process.
Throughout the testing process, ASD detects the issue and changes the code accordingly, which enhances the software quality.
ASD creates a collaborative environment among stakeholders, which promotes understanding.
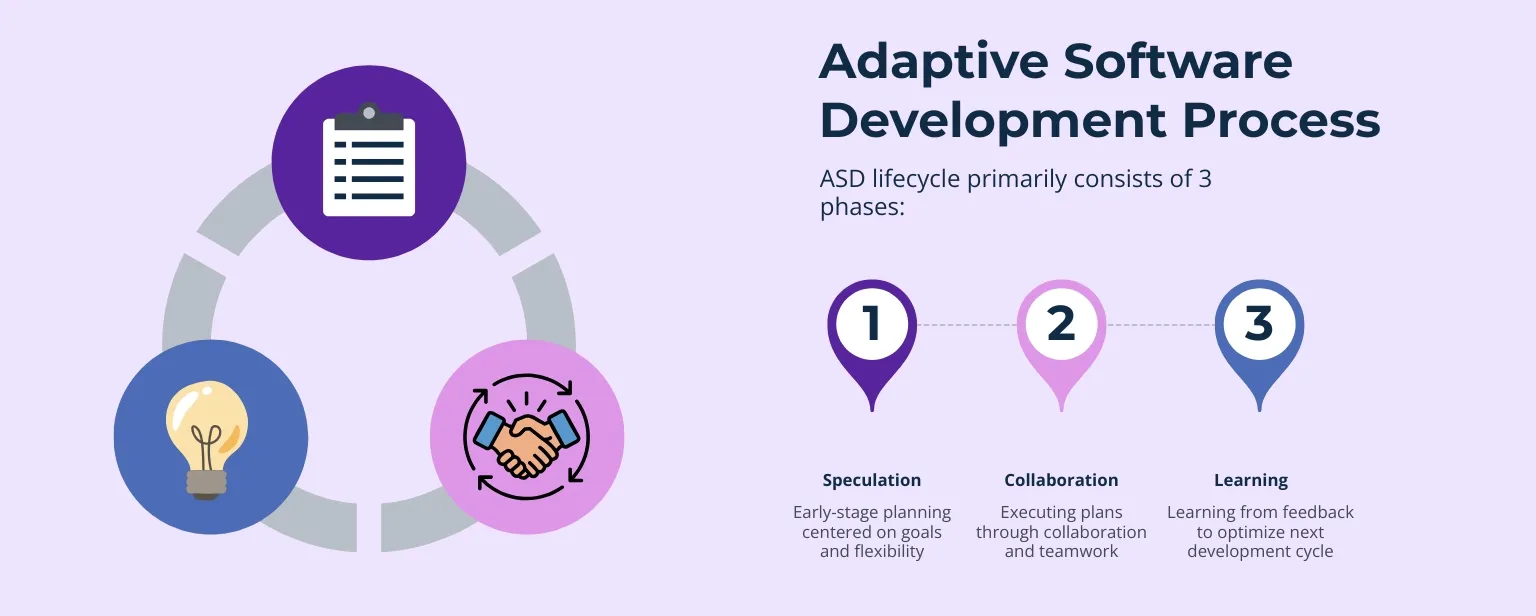
ASD lifecycle primarily consists of 3 phases:
It is the initial stage of the development process that replaces the traditional rigid planning phase. In this process, all stakeholders, including developers, managers, and consultants, analyze the vision of the software. This phase doesn’t go into detail about software and its characteristics but focuses on the main functions to make changes and for better planning.
Whatever is planned in the initial phase of speculation will be executed here. Different development teams bring their expertise and resources to the common platform to build robust applications. Executing the plan requires communication and teamwork, which directly improve development.
Learning is an essential part of an adaptive software development model. All stakeholders work on the executed part and see what users like or what feedback is. Open interactions and communication lead to better optimization of software. Teams conduct retrospectives to document learnings and update process guidelines for the next cycle.
Note: These phases are cyclic and iterative, not linear. The output of “Learning” feeds back into “Speculation.”
Adopting adaptive software development will open new growth opportunities for your software. Here are the benefits of adopting ASD:
Businesses want their software to be upgraded along with the new technology and features. They started to adopt ASD to keep software updated with newly launched features and products. This will ensure the top ranking in the competitive market.
The key feature is that ASD creates teams that work and build together. Sharing, learning, and adapting together will enhance software development quality. The team includes all stakeholders, like designers, developers, consultants, and more, for better development.
ASD focuses on customer feedback, and teams of stakeholders are continuously working according to the feedback. Improving software development.
ASD prevents risks by identifying early threats during the development process. It also minimizes the chances of project failure.
Beyond the features and benefits, ASD has some weaknesses also:
To implement ASD efficiently, a skilled team is required, which is expert and familiar with ASD principles.
Managing all rapid iterations and changes can be difficult, especially for larger projects.
The flexible results of ASD may arise from some changes in technology, code, or anything. If it can’t be managed properly, then it results in scope creep.
ASD completely relies on customer engagement. If a customer is not available or engaged, then ASD may not give benefits in development.
To implement the principles of ASD efficiently in your software development process, it is crucial to follow the best way to implement:
It is essential to cooperate with team members. Bring your team on board and discuss with them the plan, strengths, and weaknesses. The development process requires many approvals and resources, so it is mandatory to involve your team and heads in the process.
Everything depends on your team’s work and how dedicated they are to the success of ASD. To achieve better outputs, you need to create a free flow of information between designers, developers, and other team members.
The ASD model is about executing the plan and improving for the better. Encourage the team to work strongly on projects and experiment with new ideas to understand what doesn’t work.
Follow structured and strategic steps to ensure seamless and adaptive development. At the same time, instead of using long-term processes and plans, use short-term strategies and a flexible roadmap.
ASD prioritizes customer needs and wants. Incorporate features and services based on user feedback. Bring customer requirements within the development process to ensure better services and outputs.
Scrum board for visibility in ASD is a tool that refines the core ASD standards for speculation, collaboration, and learning phases. This provides transparency in the development process, nurturing continuous learning.
The CI/CD pipeline automates the development cycle through integrating and testing code continuously and executing it for faster development. In ASD, this automation is crucial to respond to changes quickly.
Version control systems like Git are crucial in ASD methodologies, as they provide infrastructure to manage changes and smooth collaboration.
| Feature | ASD | Agile | Waterfall |
| Approach | Focus on adapting to change by learning and collaboration | Focus on rapid delivery and flexibility | Linear and sequential, with a focus on development |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, designed to adapt to changes quickly | Highly flexible, allows for changes | Very rigid, difficult to change, and costly in implementation |
| Best for | Complex projects and requirements to change | Projects that require rapid deliveries, flexibility, and changing requirements | Projects with clear, fixed, and well-defined requirements |
| Customer involvement | Requires collaboration and learning with the customer | Require close collaboration and continuous feedback from the customer | Require limited customer involvement |
| Risks | Risk can be mitigated through continuous learning and adaptation | Risk can be minimized through frequent testing and feedback. | Highly risky, chances of project failure if requirements are not understood in the initial phase |
Adaptive Software Development (ASD) is a powerful methodology for managing complex and evolving software projects. Its user-centric and adaptive approach enables businesses to respond effectively to changing requirements while continuously improving product quality. By addressing potential challenges early and integrating new features through iterative learning, ASD ensures long-term performance and scalability.
At Telepathy Infotech, we help businesses implement Adaptive Software Development with the right balance of flexibility, strategy, and technical expertise. As a trusted custom software development company, our team collaborates closely with clients to reduce risks, accelerate delivery, and build future-ready solutions aligned with business goals. With a strong focus on user experience, continuous improvement, and modern development practices, we empower organizations to achieve reliable and high-performing software through ASD.
Content Writer